As we navigate further into the 21st century, the business world continues to evolve at an astonishing pace. Adapting to this continuous change is not just about adopting the latest technology but also about fundamentally rethinking how we do business. Enter Business Process Reengineering (BPR) is an essential practice for companies seeking to stay competitive and agile in 2023 and beyond.
What is Business Process Reengineering?
Business Process Reengineering (BPR) is the procedure of rethinking and reconstructing a company’s business activities in order to boost efficiency, reduce costs, and improve product or service quality.
BPR involves a fundamental reassessment of business processes, with the goal of identifying and implementing changes that will streamline operations, eliminate redundant or unnecessary activities, and create a more agile and flexible organization. The process typically involves a thorough analysis of existing processes, mapping out how they work, and identifying areas where improvements can be made.
To do this, process reengineering first recommended rethinking how the organization operates, and hence its operations, as profoundly as possible, challenging all assumptions and established traditions. The aim was to improve customer service, offer better products, reduce operating costs, and increase competitiveness, even making radical changes.
Such a radical approach came under heavy criticism, based on some resounding failures and misuse of the discipline (source: Wikipedia). From then on, it was accepted that “not everything old is so bad”, and the approach was softened. Work began on optimizing existing processes, but with a focus on continuous improvement and not on introducing such radical changes. This evolved approach is now also known as Business Process Management (BPM).
The benefits of Business Process Reengineering
There is no single list of benefits that reengineering a process will bring to the organization since this will depend on the efficiency of the current process, the maturity of the organization, the expected benefits, and the reengineering team. But we can summarize in the following list, some of the typical benefits that we have found in organizations all over the world that successfully reengineered their business processes:
- Increased efficiency by rethinking and redesigning business processes. It is quite common to find unnecessary or redundant steps that can be eliminated, as well as tasks that can be assigned to less costly roles. If the redesign of processes is accompanied by their automation in a BPM Suite, processing times and costs will also be reduced.
- In line with the previous point, when processes are reviewed it is possible to eliminate errors, and thus increase the quality of the process output, and therefore the associated products or services.
- If the implemented changes are successful, it will increase customer satisfaction, and eventually also supplier satisfaction. The latter can lead to a reduction in costs, with a direct impact on the company’s competitiveness and profitability.
- By business process design, the organization will also be better adapting to the market, customer needs, regulatory changes, etc. In this sense, using no-code tools such as Flokzu, allows the initial BPR definition of processes to be faster, but also their evolution and modifications that will be surely necessary in the (near) future.
- Finally, but very importantly, getting involved in a process redesign and process improvement process is a key motivating factor for the whole team. They will feel empowered to improve their processes, and engaged which will surely improve their morale, satisfaction, and productivity.
Principles of Business Process Reengineering
The focus of BPR is on creating a customer-centric approach to business processes, with the aim of delivering products or services that meet the needs of customers in the most efficient and effective way possible. This often involves the use of new technologies and automation, like Cloud-BPM Suites such as Flokzu for process automation and improvement, as well as changes to organizational structure and management practices.
BPR can be a complex and challenging process, requiring a significant investment of time, resources, and expertise. However, when done correctly, it can result in significant benefits for organizations, including increased productivity, improved customer satisfaction, and enhanced competitiveness in the marketplace. However, in recent years, no-code and low-code technology have made it possible to significantly reduce the time required to automate a redesigned process. And in this way, costs have also been significantly reduced, allowing processes that were previously “untouchable” to be implemented in a short time in a cloud BPM tool such as Flokzu.
4 steps of Business Process Re-engineering (BPR)
The 4 main phases of a business process re-engineering initiative are Diagnosis, Analysis and evaluation, re-engineering, and Evaluation. This is a virtuous cycle that should restart over and over.
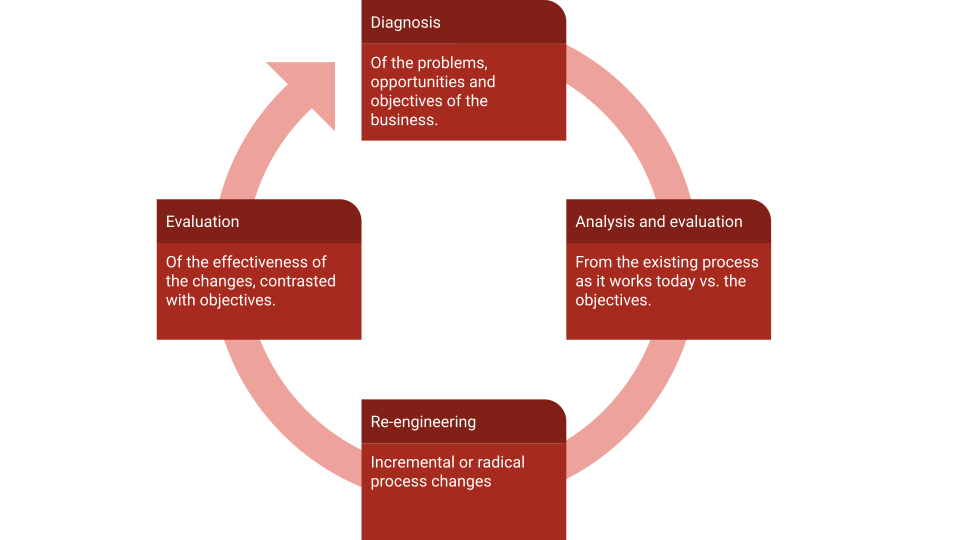
Diagnosis of problems and opportunities
In this phase, the current business processes are analyzed to identify areas that need improvement. This involves gathering data on current processes (being they manual or automated in a BPM Suite), understanding how they work, and identifying areas of inefficiency, redundancy, or waste.
Analysis and evaluation of the existing process
Once the diagnosis phase is complete, the analysis phase begins. During this phase, the data collected in the diagnosis phase is analyzed to identify the root causes of the problems in the current processes. The analysis phase involves breaking down the current processes into their component parts, identifying process bottlenecks, and analyzing the flow of work through the organization. If the process performance is being measured using KPIs, then they are a key input to detect where the problems are.
Process reengineering and redesign
The re-engineering phase involves redesigning the business processes to eliminate inefficiencies, streamline workflows, and reduce costs. This may involve reorganizing work activities, introducing new technology, changing job responsibilities, and modifying business rules and policies.
No-code technologies play a key role here, allowing processes to be quickly modeled, tested, and deployed in production. Avoiding coding and complex configurations in the software to automate processes significantly reduces the time consumed, and the associated costs and motivates the team by showing tangible results quickly.
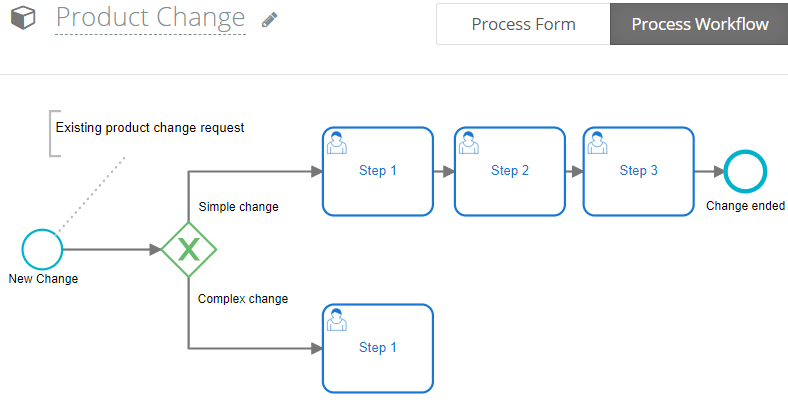
To redesign the process, you will need a graphical and formal representation. It will be useful to discuss the process with your team and share it with stakeholders. Whether you use the worldwide standard, BPMN, or another, a clear map of the new process will be available, to understand and discuss it.
Finally, you may send the model to a process engine to run it. This is the implementation step of the new redesigned and automated process. You will run it in a business process management system (BPMS) like Flokzu.
Below is a (very simple) example of a Manufacturing process, to manage product changes, modeled with the BPMN standard in Flokzu BPM Suite:
Effectiveness evaluation and corrections
This is the final phase when the results of the re-engineering effort are evaluated to determine the success of the project. The evaluation phase involves measuring performance against the benchmarks established in the planning phase, identifying areas where further improvements are needed, and ensuring that the changes made during the re-engineering phase are sustainable over time.
BPR Methodologies
There are few BPR methodologies that have been developed over the years. The main reasons why there are many methodologies for reengineering business process are:
- BPR is a complex and multifaceted discipline that involves the redesign of business processes that can be very complex. Moreover, these processes can involve multiple departments, business units, customers, suppliers, machines, and IT systems. Therefore, there are different approaches, each with its own tools, techniques, and strategies.
- Different industries have different needs. For example, a BPR methodology that works well in the manufacturing industry may not be suitable for a public hospital. Therefore, different industries have developed their own BPR methodologies tailored to their specific needs.
- BPR has evolved over time, with new methodologies and approaches emerging as practitioners have gained more experience and expertise. As a result, there are many different BPR methodologies that reflect this evolution and incorporate new tools and techniques.
- Different experts have different points of view: BPR has been studied and practiced by a variety of experts, including management consultants, academics, and business leaders. Each of these groups may have their own view on how best to approach BPR, leading to the development of different methodologies.
The following is a description of some of the main and most widespread process reengineering methodologies.
Hammer and Champy’s methodology
This methodology was introduced by James Champy and Michael Hammer in their 1993 book, “Reengineering the Corporation.” It involves a radical redesign of business processes that is driven by a focus on customer needs and supported by new technology.
The Davenport Methodology
This methodology was developed by Thomas Davenport in his 1993 book, “Process Innovation.” It emphasizes the need for a thorough understanding of the current processes, as well as the use of analytical tools to identify areas for improvement.
Manganelli and Klein’s methodology
This methodology was introduced by Ron Manganelli and Michael Klein in their 1994 book, “The Reengineering Handbook.” It emphasizes the importance of involving employees in the reengineering business processes, as well as the need for strong leadership and a clear vision for the organization’s future.
Kodak’s methodology
This methodology was developed by Eastman Kodak Company in the 1990s as part of its successful reengineering efforts. It involves a structured approach to process redesign that includes identifying customer needs, benchmarking against competitors, and using cross-functional teams to redesign processes.
Other methodologies
BPR methodologies include the Six Sigma approach, the Lean methodology, and Total Quality Management (TQM). Each of these methodologies has its own unique approach and tools for achieving process improvement and organizational transformation.
A real-life example of BPR
BPR examples: widely used in the literature to describe a concrete example of successful BPR is related to the Ford Motor Company. This case clearly exposes most of the facets of BPR discussed above.
The case of Ford Motor Company is about the purchasing department. In the early 1990s, Ford’s purchasing department was facing several challenges, including slow processes, high costs, and low supplier satisfaction. Ford’s leadership recognized the need for a major overhaul of the department’s processes and turned to BPR as a solution.
The BPR project involved a complete redesign of the purchasing process, including the introduction of new technology, the consolidation of purchasing functions, and the adoption of a supplier development program. The project also involved extensive employee training and communication to ensure that all stakeholders understood the new processes and were on board with the changes.
The results of the BPR project were impressive. Ford was able to reduce the purchasing process cycle time by 70%, resulting in faster delivery of parts to production lines. The project also reduced purchasing department headcount by 30%, resulting in significant cost savings. Supplier satisfaction increased from 35% to 85%, and supplier defects were reduced by 90%.
Overall, the BPR project helped Ford’s purchasing department become more efficient, cost-effective, and customer-focused, and it contributed to the process in company and overall its success in the highly competitive automotive industry.
When should you consider BPR?
Business Process Reengineering is a major undertaking that requires significant time, resources, and investment. As such, it should be considered in situations where there is a strong need for process improvement and organizational transformation. Here are some situations where BPR may be appropriate:
- When a radical improvement in a process is needed. This may be because existing processes are obsolete, inefficient, or unable to meet customer needs.
- When it is necessary to reduce costs: When competitiveness is lost due to process costs, it is time to redesign processes and eliminate unnecessary costs by eliminating steps, automating processes with BPM tools such as Flokzu, and streamlining workflows.
- When it is necessary to improve the quality of products or services by identifying and eliminating sources of errors and inefficiencies in the processes.
- When it is necessary to respond to changes in demand, competition, or regulations. This is when BPR is combined with no-code technologies to implement these changes with agility.
- When it is necessary to integrate new technologies into processes, identify new ways of using technology to automate and streamline workflows.
Overall, BPR should be considered when there is a strong need for significant process improvement and organizational transformation, and when there is a willingness to invest the necessary time, resources, and effort to achieve these goals.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Implementing a successful Business Process re-engineering project can be a challenging task. Here are some common pitfalls that we at Flokzu have seen in different companies worldwide:
- The leadership team must be fully committed to the BPR project and communicate the importance of the project to the rest of the organization. If the leadership team is not fully committed, the project may fail.
- Communication and training are critical to the success of a BPR project. All stakeholders must be informed about the project, its objectives, and its potential impact on the organization. Adequate training must also be provided to ensure that employees are prepared for the new processes.
- Resistance to change is a common pitfall in BPR projects. To avoid this, it is essential to involve employees in the project from the outset and to communicate the benefits of the project to them. Using intuitive business process reengineering tools with a user-friendly UI, such as Flokzu, will facilitate the adoption of new technologies, reducing resistance. Once users see the value of the new tools, they will lead by example by facilitating organization-wide adoption.
- BPR projects should always focus on the needs of the customer. Failure to do so may result in processes that are inefficient and fail to meet customer needs.
- Using the wrong technologies. If we are looking to show results quickly, embarking on custom software development projects is not a good idea. Preferring no-code technologies will allow you to iterate much faster and deliver results faster.
- Organizational culture plays a significant role in the success of a BPR project. To be successful, the project must align with the organization’s culture and values.
- BPR projects can be time-consuming and complex. Unrealistic timelines can lead to rushed implementation and potential failures. It is essential to establish a realistic timeline for the project and ensure that all stakeholders are aware of it. Here again, using no-code tools, tested worldwide and ready to be used, reduces project times and risks.
- It is important to establish metrics to measure the success of the BPR project. Without proper measurement and evaluation, it may be difficult to determine the impact of the project and identify areas for improvement.
Conclusions
We can conclude that Business Process Reengineering (BPR) is a methodology that organizations can use to radically (or not so much) improve their business processes, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. BPR involves four main phases: Diagnosis, Analysis, Reengineering, and Evaluation.
There are several BPR methodologies, including Hammer/Champy, Davenport, Manganelli, and Kodak, and the selection of the appropriate methodology depends on the organization’s needs and goals.
Implementing a successful BPR project requires leadership commitment, effective communication, and training, focus on the customer, attention to organizational culture, realistic timelines, and proper measurement and evaluation. Failure to address these factors can result in common pitfalls that can hinder the success of the project.
Choosing the right process automation tools is key. Using a no-code BPM Suite, such as Flokzu, proven worldwide and very agile, will allow you to show results quickly and reduce the risks associated with software development and the use of complex traditional tools.
Overall, BPR can be a powerful tool for organizations seeking to improve their processes, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction, but it requires careful planning, execution, choosing the right software tools, and ongoing evaluation to achieve success.
FAQs
What is meant by Business Process Reengineering?
Business Process Reengineering (BPR) refers to a radical redesign of core business processes to substantially improve productivity, efficiency, and quality. The BPR approach involves fundamentally rethinking the business processes, discarding the old, inefficient methods, and constructing novel ways to perform the same tasks, often leveraging modern technologies. It’s a strategic initiative to improve customer satisfaction and business outcomes by transforming how work is completed.
What are the 3 R’s of Business Process Reengineering?
The 3 R’s of Business Process Reengineering (BPR) are Reengineering, Redesign, and Rebuild. These are key stages in the BPR life cycle. Reengineering involves identifying and analyzing current processes that need improvement. ‘Redesign’ is the stage of rethinking and remodeling these processes for optimal efficiency and effectiveness. Lastly, ‘Rebuild’ is the implementation stage where the redesigned processes are deployed, transforming how the organization operates to achieve significant performance enhancements.
Why is BPR important?
Business Process Reengineering is vital because it aids organizations in making significant advancements in their efficiency, productivity, and quality of service. By fundamentally rethinking and redesigning business processes, BPR eliminates inefficiencies and redundancies, fostering streamlined operations. It can lead to cost savings, improved customer satisfaction, and competitive advantage. By adapting to changing business environments through BPR, organizations can stay relevant, innovative, and ahead of their competitors in today’s dynamic marketplace.
What is the benefit of BPR?
The benefits of Business Process Reengineering are manifold. It enables enterprises to drastically improve operational efficiency while also lowering expenses and enhancing service quality. By eliminating unnecessary processes and streamlining workflows, BPR can improve productivity and faster turnaround times. Additionally, it can increase customer satisfaction through better service delivery. By facilitating innovation, BPR can also help companies gain a competitive advantage, making them more agile and responsive to changing market conditions.
Would you like to learn how you can automatize your processes? We invite you to schedule a meeting with one of our experts, so we can automate together a complete process, and improve your organization.





























